ESE5160_T05-Fusion-Maverick_Magic-Wand
a14g-final-submission
* Team Number: T05
* Team Name: Fusion Maverick
* Team Members: Qingyang Xu, Ruizhe Wang, Xinyi Wang
* Github Repository URL: https://github.com/ese5160/a14g-final-submission-s25-t05-fusion-maverick.git
* Description of test hardware: (development boards, sensors, actuators, laptop + OS, etc)
1. Video Presentation
2. Project Summary
Device Description
We designed a magic wand for IoT-based environments, capable of remotely controlling electronic devices through gesture recognition. In our prototype, we used a motor and an LCD screen as actuators. The system also features an “echo back” mechanism, providing distinct haptic feedback via a haptic driver and vibration motor to confirm command execution.
The project is inspired by the current smart home system. Instead of the mobile control via smart phone, we want to bring in more fun in the whole scheme. In addition, the magic wand could also be programmed as a laser cat teaser or a magic wand for children entertainment.
Device Functionality
-
Design of the Internet-Connected Device:
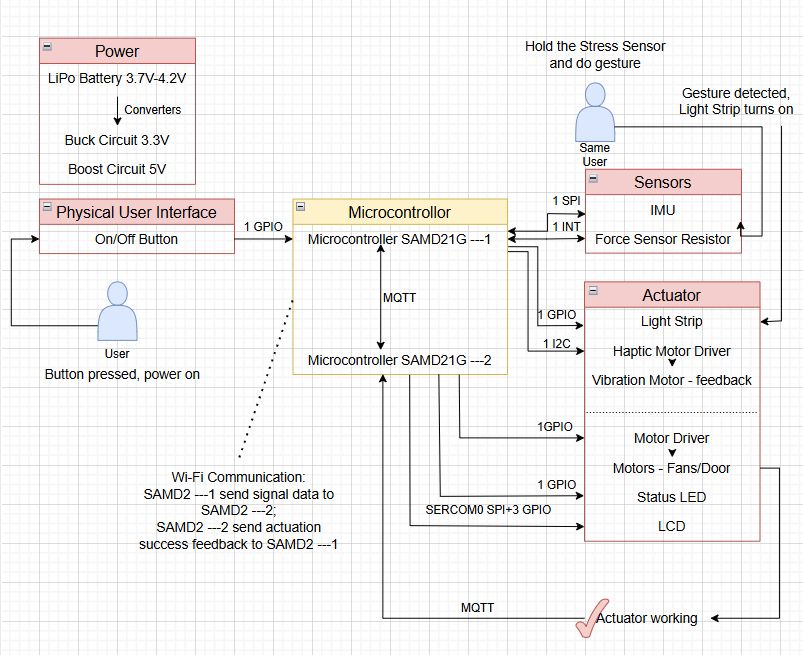
The system is composed of two custom-designed PCB modules: the Wand Module and the Actuator Module.
The Wand Module detects hand gestures using an onboard IMU and activates only when the force-sensitive resistor (FSR) is pressed, minimizing unintended gesture recognition.
Once a gesture is recognized, the microcontroller processes the data and transmits the corresponding command to the cloud via Wi-Fi.
The Actuator Module, which maintains an active Wi-Fi Internet connection, receives this command and performs the appropriate action using motor and LCD.
After execution, the actuator sends feedback to confirm task completion, which is communicated back to the user via a vibration motor on the wand.
-
Sensors, Actuators, and Key Components:
-
Magic Wand PCB:
- Slide Switch – Powers the wand on/off.
- Force-Sensitive Resistor (FSR) – Enables gesture recognition only with intentional input.
- Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) – Detects motion and captures gesture patterns.
- NeoPixel LED Strip – Provides visual animation feedback upon command transmission.
- Vibration Motor – Delivers haptic feedback when a task is confirmed as complete.
-
Actuator PCB:
- LCD Screen – Displays animations or task-related visuals.
- Motor – Executes the received command from the wand module. The speed can be changed.
- State LED – Indicates task activity status (on during task execution, off when idle); also serves as a debugging tool.
-
Challenges
The difficulties we encountered lies in two aspects: MQTT communications between two devices with the introduction of Node-RED and the stack/memory allocation among different threads/tasks.
For the MQTT communications problem, we aimed to achieve both end-to-end/device-to-device control and cloud control, then we need to tackle with the potential conflicts. We modified the Node-RED interface setting(specifically, function with multiple buttons architecture) to allow both control scheme and ensure no mutual influence against each other.
For the stack/memory allocation challenge, we mainly resolved by using the debug mode and Percepio to measure the CPU usage of each thread/task and their occupation with respect to the whole progress, so that distribute adequate stack/memory for each thread/task.
Prototype Learnings
-
Lessons learned:
We learned the importance of early testing with real hardware and dev board for all sensors and actuators. Also we learned the importance of planning for edge cases and hardware redundancy. For example, we added test pads to unused pins so they could serve as backups if any primary connections failed.
-
What we would do differently:
We would try to use DMA for SPI communication when wrting the LCD library. We would also design the 3D-printed parts earlier to make them better fit our PCBs. We might also design two firmware versions so that we can see the difference when we update the OTAFU.
Next Steps & Takeaways
-
Steps to Finish/Improve the Project:
We plan to refine the IMU gesture recognition algorithm using machine learning models to improve accuracy. We also aim to optimize the firmware architecture by consolidating all tasks into Wi-Fi-related modules. This restructuring is expected to reduce memory usage and potentially resolve the system freeze issue.
-
What We Learned in ESE5160:
This project significantly deepened our understanding of embedded IoT systems, covering the entire development cycle—from PCB design and sensor integration to firmware development and real-world testing. Through hands-on experience, we gained a better appreciation of the challenges involved in building reliable and user-friendly connected devices. It not only reinforced our theoretical knowledge but also sharpened our practical engineering skills, such as FreeRTOS task scheduling and hardware-software interfacing. Most importantly, we developed strong debugging capabilities, learning how to systematically identify issues using debug mode, an oscilloscope, or a logic analyzer, trace root causes, and implement effective solutions under real-world constraints.
Project Links
- Node-RED URL: http://52.191.130.70:1880/.
- Node_RED UI: http://52.191.130.70:1880/ui/.
- Altium 365 Workspace_Magic Wand: ESE5160_T05_magic-wand.
- Altium 365 Workspace_Actuator: ESE516_T05_actuator.
3. Hardware & Software Requirements
- Hardware Requirements:
- Magic Wand PCBA:
-
HR01 - project shall be based on SAMW25 core.
-
HR02 - external-connected slide switch shall be used for activation of the wand.
-
HR03 - external-connected Force-Sensitive Resistor(FSR) Interlink Model 402 shall be used for for command detection.
The sensor will detect if continuous force exerted in the sensing area, as a start flag and maintaining state for the wand gesture recognition. - HR04 - mounted 6-axis IMU MPU6500 shall be used for for wand gesture recognition.
The sensor will collect 6-axis data(3-axis gyroscope and 3-axis accelerometer) while the FSR sensing area is continuously pressed.
The collected data shall be then used to recognize the swing trajectory of the wand for gesture recognition. The tentative way we’ve designed for gestures are:
- Gesture 1: Wave tilde—wave pattern;
- Gesture 2: Zigzag—twinkle;
- Gesture 3: Clockwise circle—Turn on the motor;
- Gesture 4: Swipe up—Speed up the motor and LCD shows volume up animation;
- Gesture 5: Swipe down—Slow down the motor and LCD shows volume down animation;
- Gesture 6: Anticlockwise circle—Turn off the motor;
- Gesture 1: Wave tilde—wave pattern;
-
HR05 - external-connected LED strip shall be used for command emission indication.
The LED strip will quickly flash simultaneously as the control command sent out via MQTT to the cloud, imitating the laser emission process. - HR06 - external-connceted vibration motor drived by DRV2605L haptic motor controller shall be used for actuator execution feedback.
The vibration motor will funtion as a feedback reponse to different actuators’ actions. The tentative way we’re going to execute it is:- LCD tasks — Vibration Motor Soft Bump - 100% (Effect NO.7);
- Motor ON/OFF — Vibration Motor Strong Click - 60% (Effect NO.2);
- Motor SPEED UP — Vibration Motor Strong Buzz - 100% (Effect NO.14);
- Motor SLOW DOWN — Vibration Motor 1000 ms Alert 100% (Effect NO.16).
-
- Acuator PCBA:
-
HR07 - project shall be based on SAMW25 core.
-
HR08 - mounted state LED shall be used to reflect the state of the actuator.
If there is no control demand, the state LED maintains off; vice versa, the state LED will be turned on when instruction send until the task execution. -
HR09 - external-connected gearmotor drived by DRV8874 motor driver shall be used as one of the actuator.
The motor will be drived to execuate the wand command. Such as clockwise to turn on, swipe up to increase the rotation speed, swipe down to decrease the rotation, and anticlockwise to turn off. -
HR010 - external-connected LCD shall be used as the other actuator.
The LCD would have two function modes, one is the visulization of motor control, which would reflect the motion state of the motor, such as, as the rotation speed increase, the LCD will display volume up animation.
In addition, the LCD would solely interact with the magic wand, such as the LCD will antimate a wave pattern when wand has a ‘Wave’ tranjectory gesture, and animate a twinkle with respect to wand ‘Zigzag’ tranjectory gesture.
-
- Magic Wand PCBA:
- SRS:
- SR01 - slide switch on/off.
- configured as an external interrupt;
- programmed state machine controlling the entire state(ON/OFF) of the system.
- SR02 - FSR based command detection.
- configured as an external interrupt;
- a FSR will be used to monitor the use condition of the wand:
- if no strain/stress detected(logic ‘high’), the wand is a common stick used for fun;
- if strain/stress detected(logic ‘low’), the wand is utilized as our proposed “magic wand”.
- SR03 - IMU-based gesture recognition.
- configued as a SPI(SERCOM0);
- the 6-axis IMU MPU6500 will be used for collecting data for one samping period when the user touches the sensing area of the strain/stress sensor;
the collected data will be used for the recognition of trajectory gestures of the wand, and then send out the correspoding control demand to the cloud.
- SR04 - LED strip based command emission.
- configued as a digital output;
- a LED strip will be programmed to flash simultaneously when the control demand is sent out after correct gesture recogonition.
Neopixel library is utilized for this implmentation.
- SR05 - actuartor execution.
- the corresponding actuator(determined by the pre-defined gestures) will response to the magic wand gesture, executing the command and then sending feedback to the cloud to actiavte the vibration motor on the wand;
- state LED, configued as a a digital output:
keep off while no command, turned on when received the command and turned off when the tasks are successfully executed. - micro metal gear motor, drived by DRV8874 motor driver, configued as one analogue output(PWM) and two digital outputs:
- activation: clockwise circle drawn by the wand;
- brake: anticlockwise circle drawn by the wand;
- accelerate: wand swipes up;
- decelerate: wand swipes down.
- LCD, configued as a SPI(SERCOM0) and several digital I/Os:
- mode 1 - visulization of motor motion state:
- motor accelerates: volume up animation;
- motor decelerates: volume down animation.
- mode 2 - intaction with wand:
the LCD would solely interact with the wand.- the LCD will animates a twinkle with respect to wand ‘Zigzag’ tranjectory gesture;
- the LCD animates a wave pattern with respect to wand ‘Wave’ tranjectory gesture.
- the LCD will animates a twinkle with respect to wand ‘Zigzag’ tranjectory gesture;
- mode 1 - visulization of motor motion state:
- state LED, configued as a a digital output:
- the corresponding actuator(determined by the pre-defined gestures) will response to the magic wand gesture, executing the command and then sending feedback to the cloud to actiavte the vibration motor on the wand;
- SR06 - vibration motor based actuator exection feedback.
- drived by DRV2605L haptic motor controller, configured as an I2C(SERCOM3) and one digital output.
- a vibration motor will be activated for about few seconds once the control demand has been successfully received and executed by the actuator. We proposed varying vibration effects/modes of the motor with respect to diffrent task accomplishment. The tentative way we’re going to execute it is:
- LCD tasks — Vibration Motor Soft Bump - 100% (Effect NO.7);
- Motor ON/OFF — Vibration Motor Strong Click - 60% (Effect NO.2);
- Motor SPEED UP — Vibration Motor Strong Buzz - 100% (Effect NO.14);
- Motor SLOW DOWN — Vibration Motor 1000 ms Alert 100% (Effect NO.16).
- SR07 - Node-RED interface and interaction.
- Node-RED interface will take in the IMU gesture and actuator motion feedback JSON MQTT messages and print out in the UI dashboard.
- In addition, we also enable Node-RED to directly control the actuator via different buttons.
- SR01 - slide switch on/off.
4. Project Photos & Screenshots
- Framework of the boards:
-
whole case:
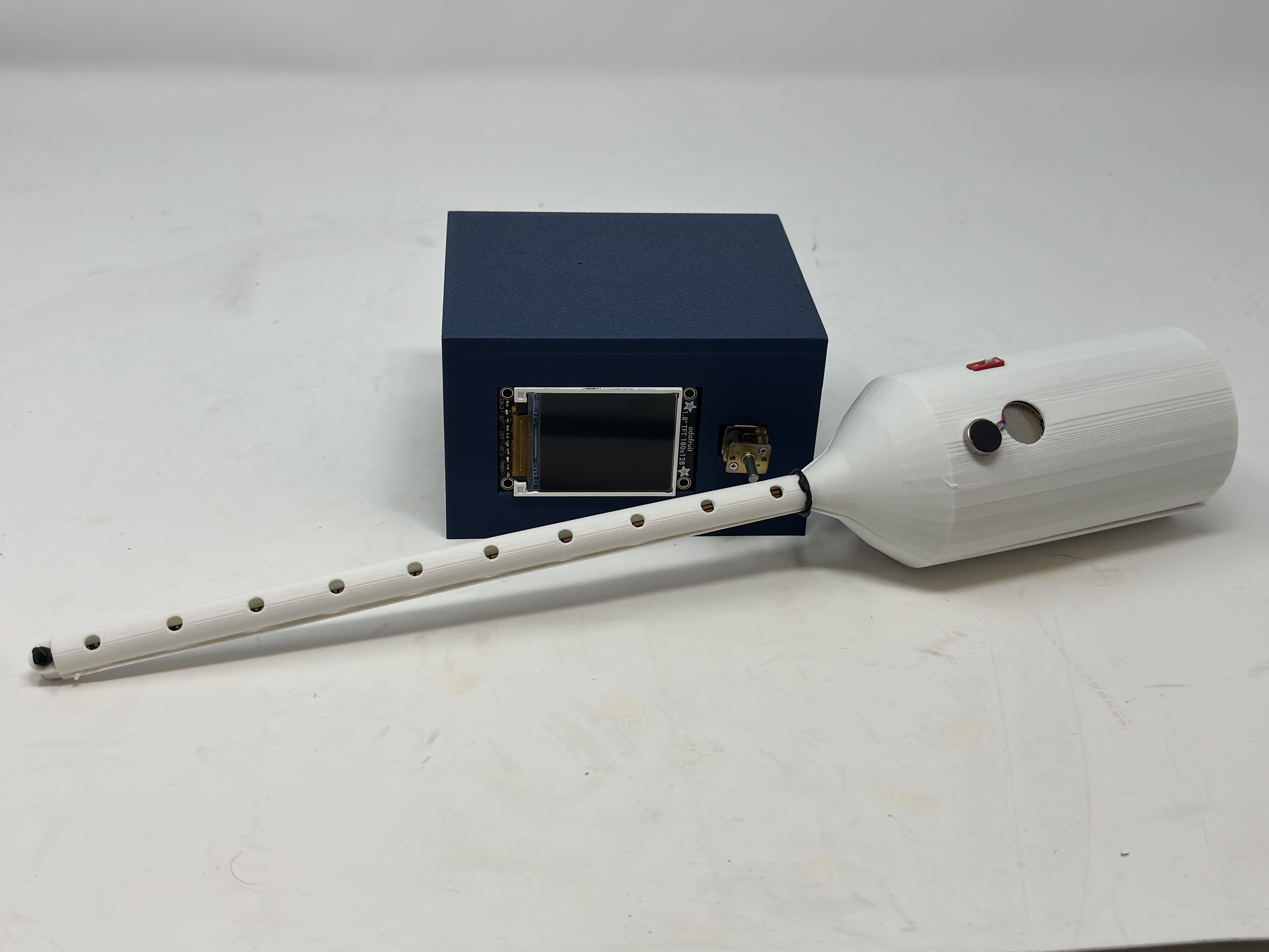
-
magic wand case and its inner:
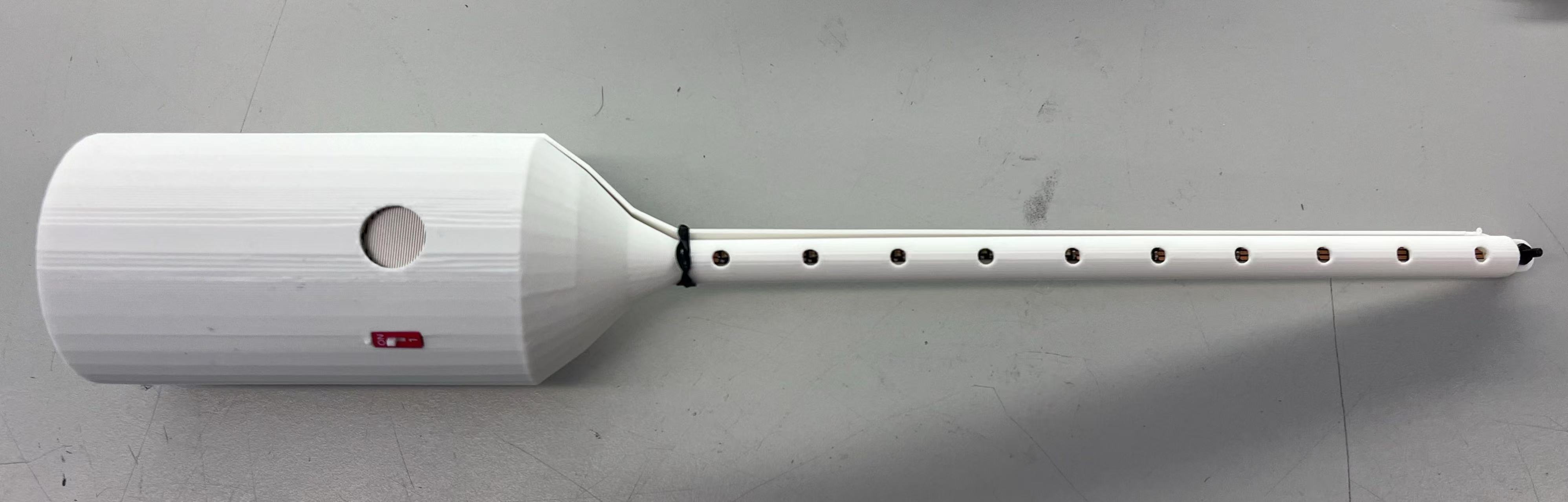

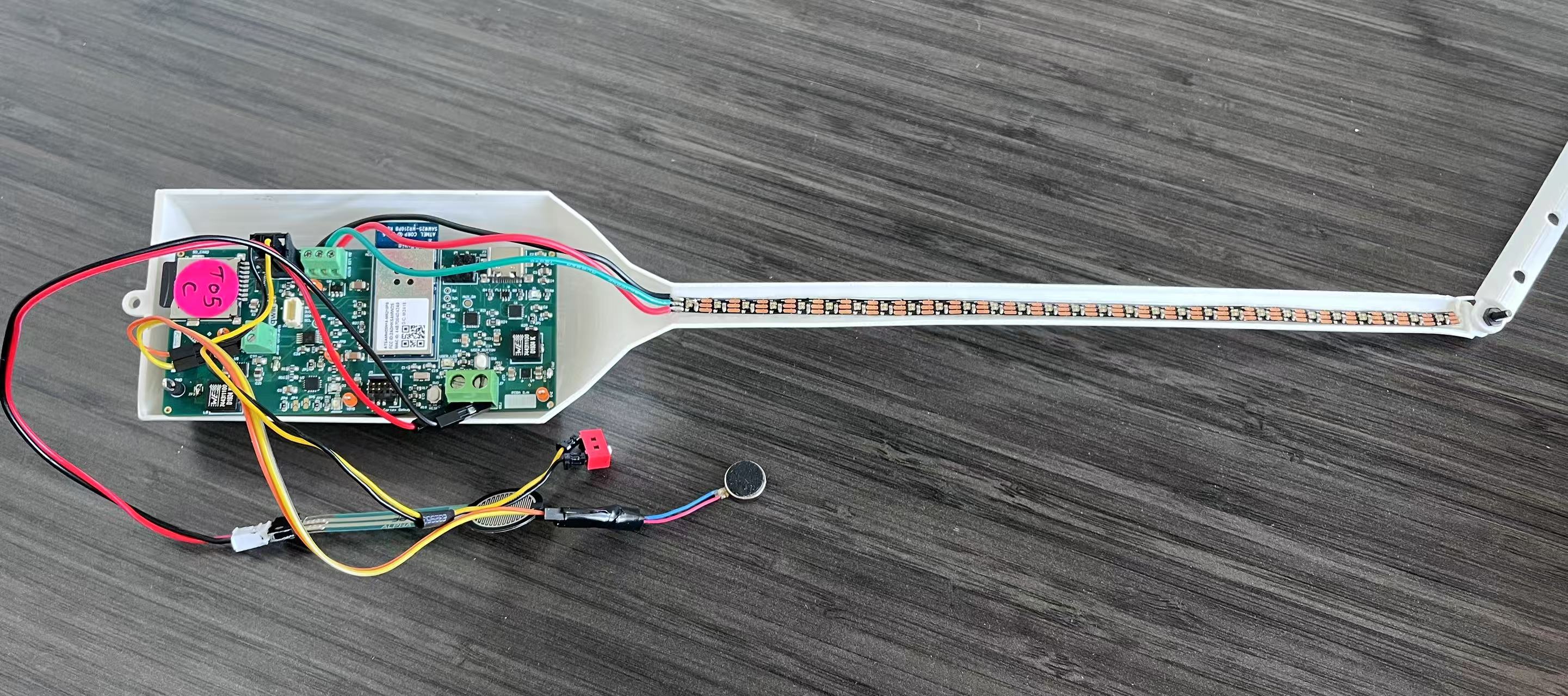
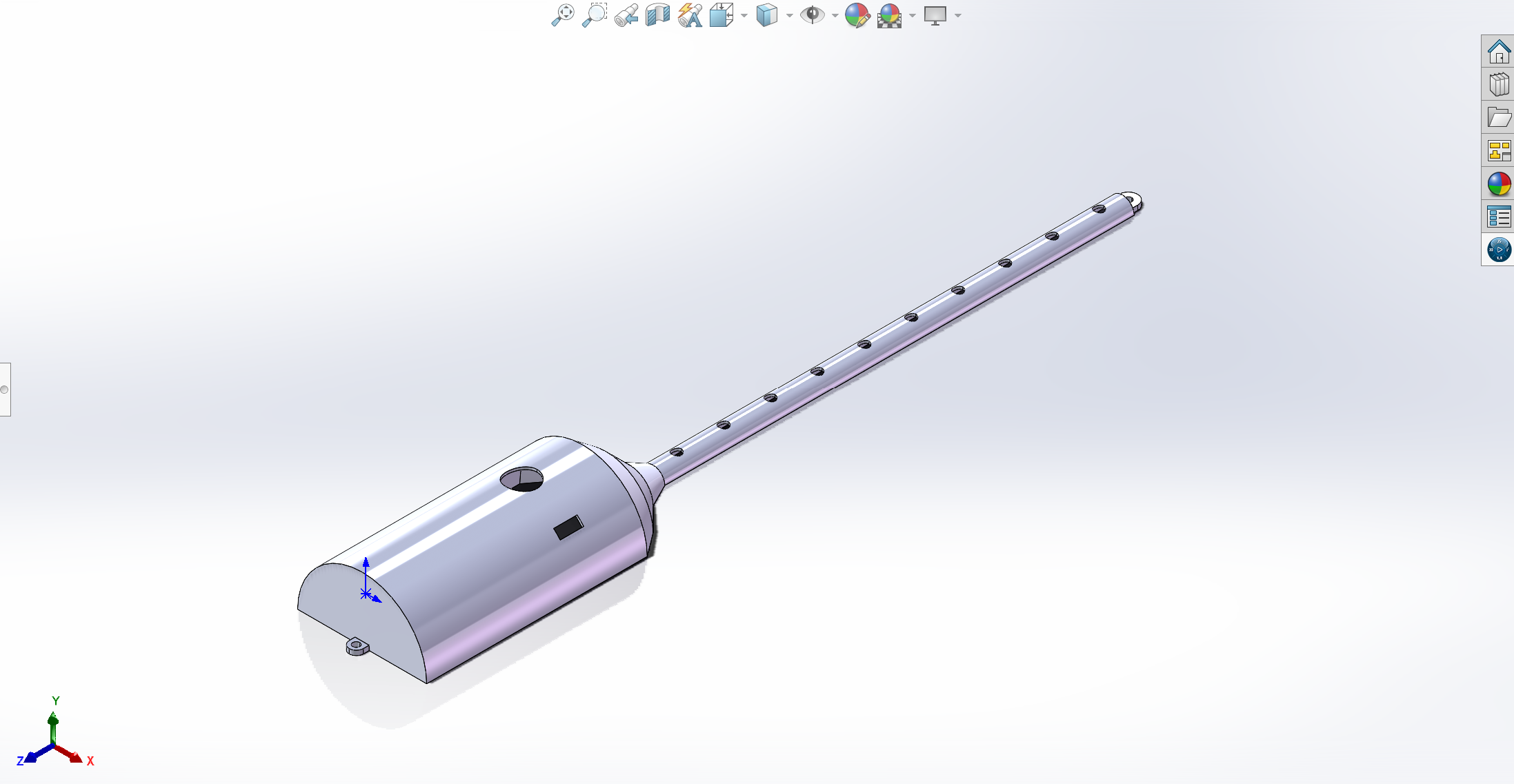
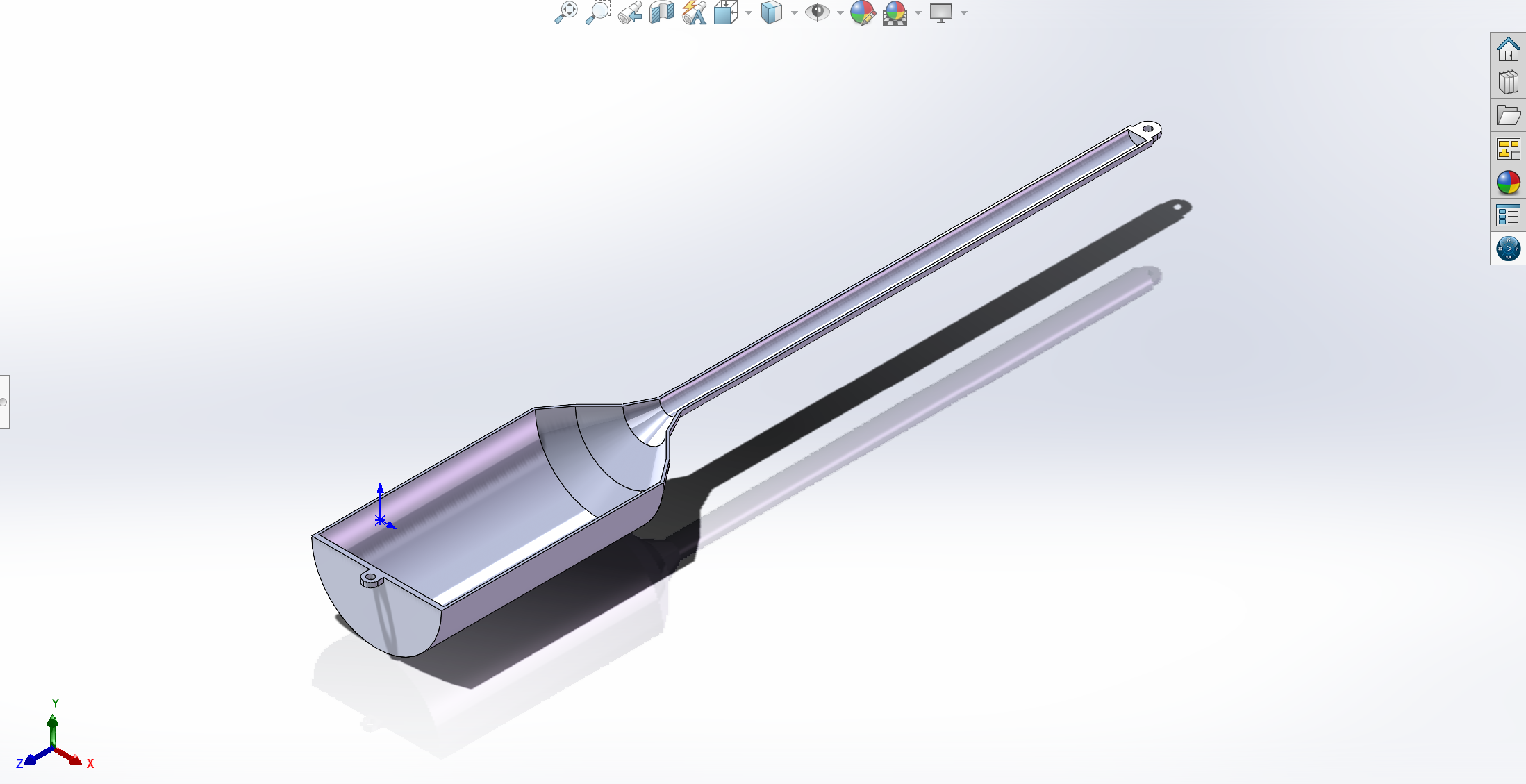
-
actuator case and its inner:
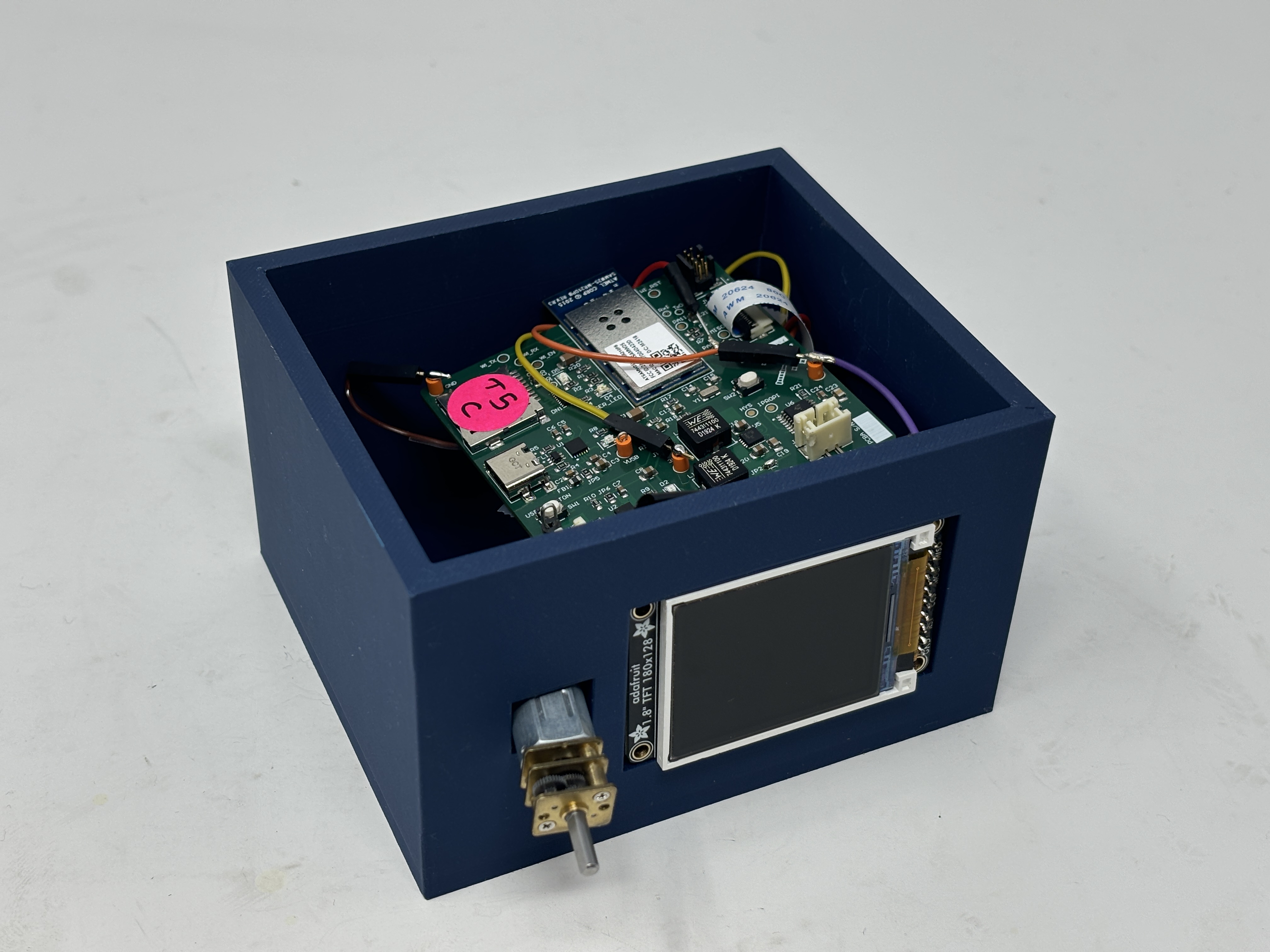
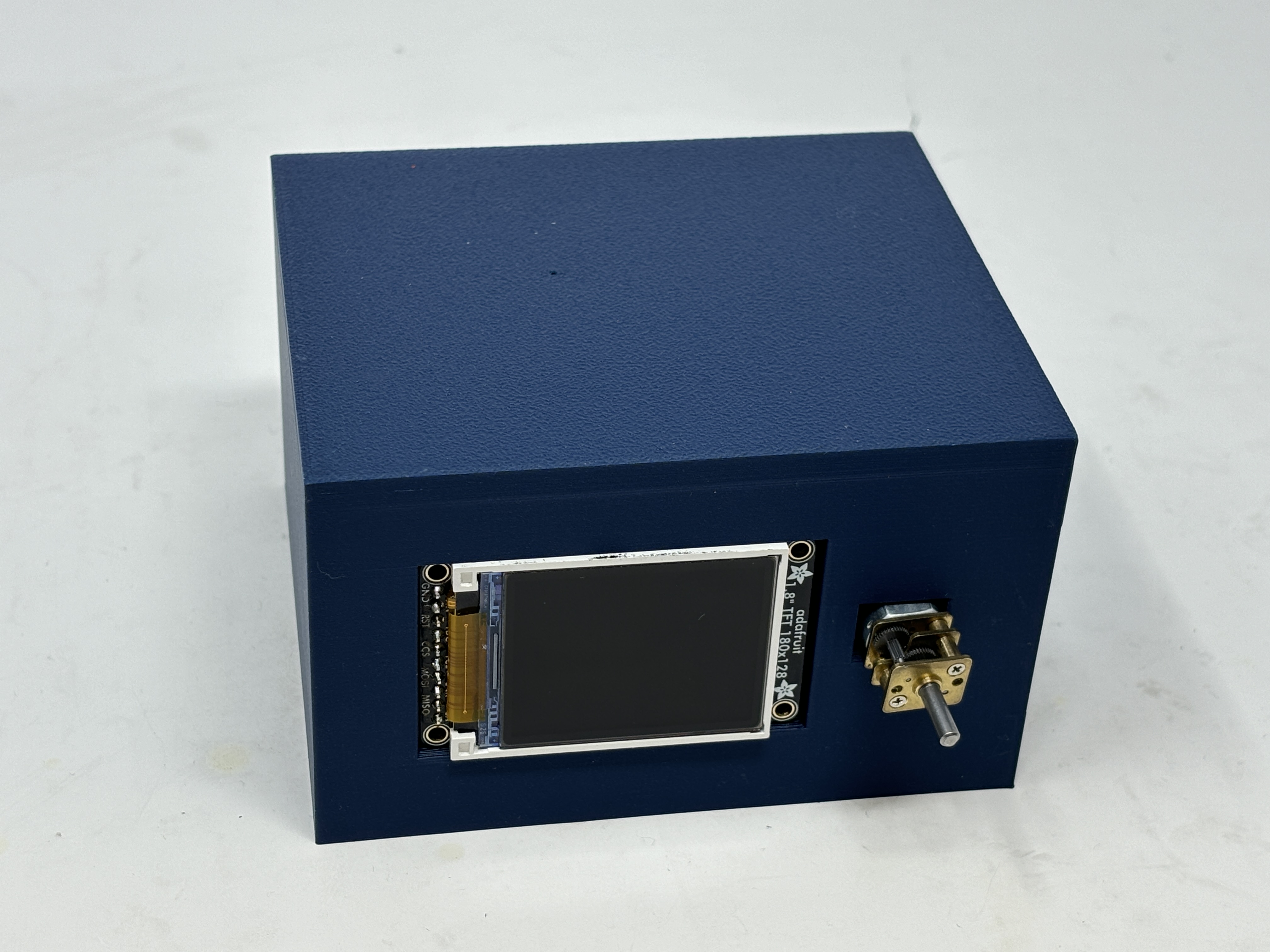

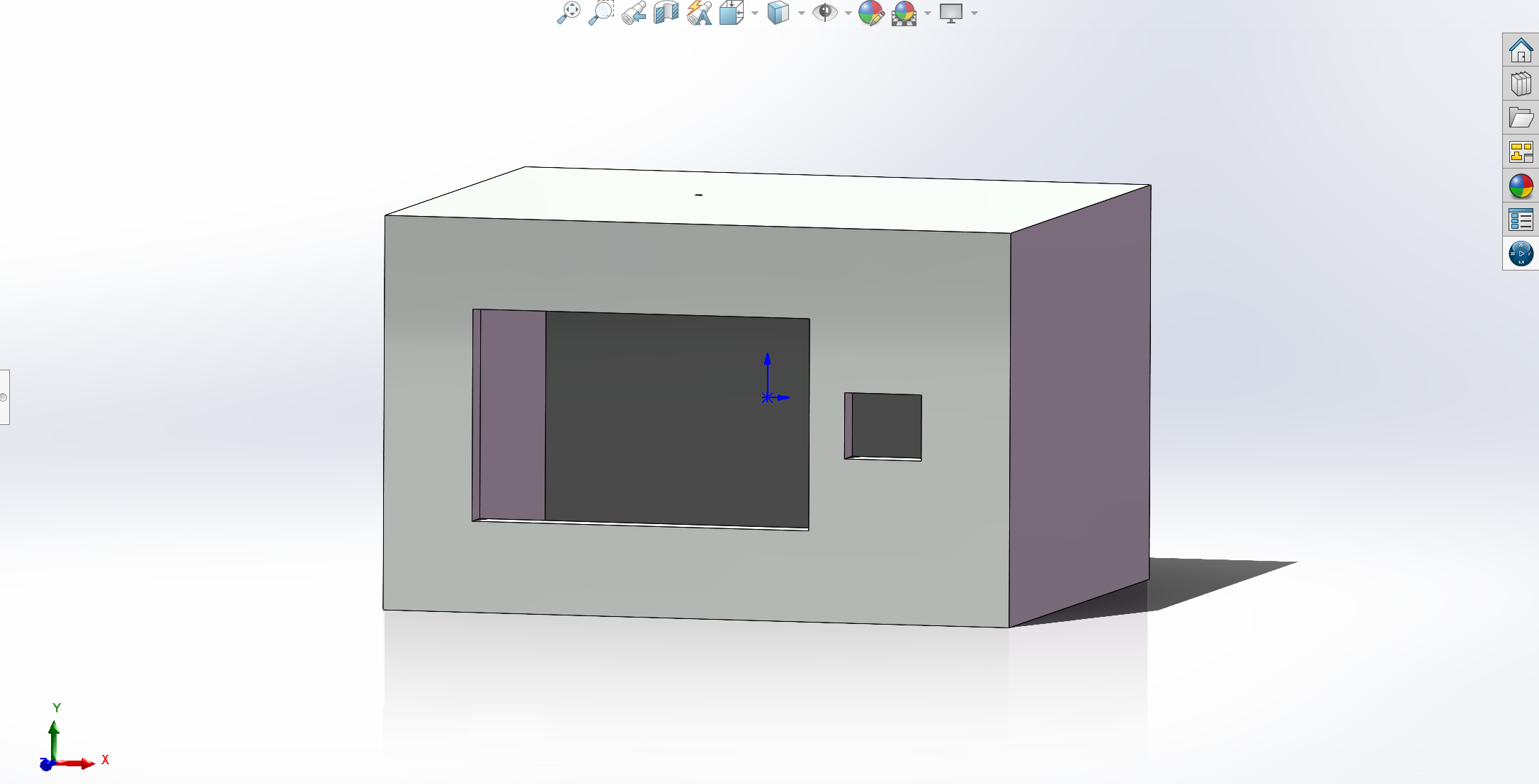
-
- The standalone PCBA, top:
-
magic wand:
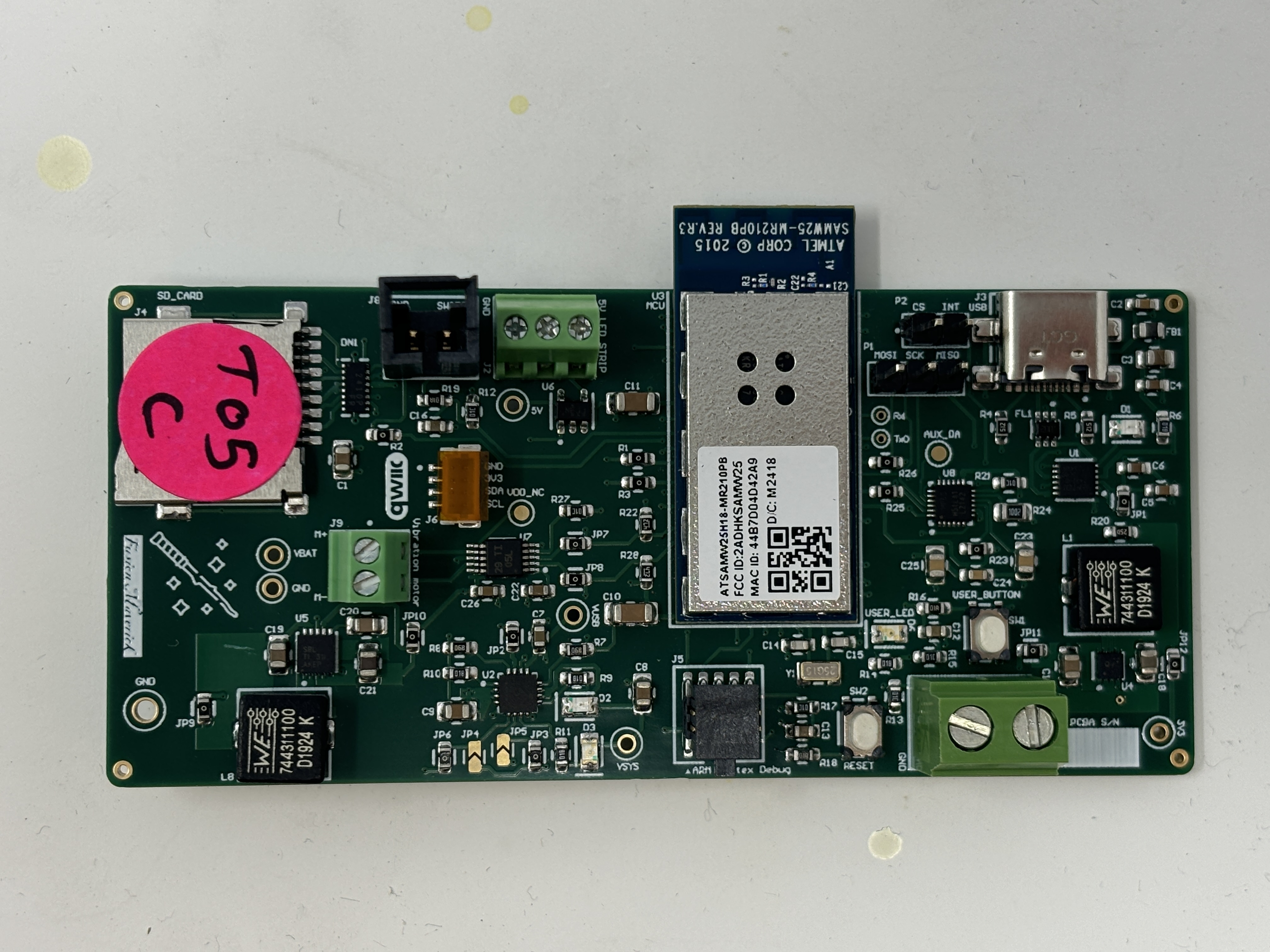

-
actuator:
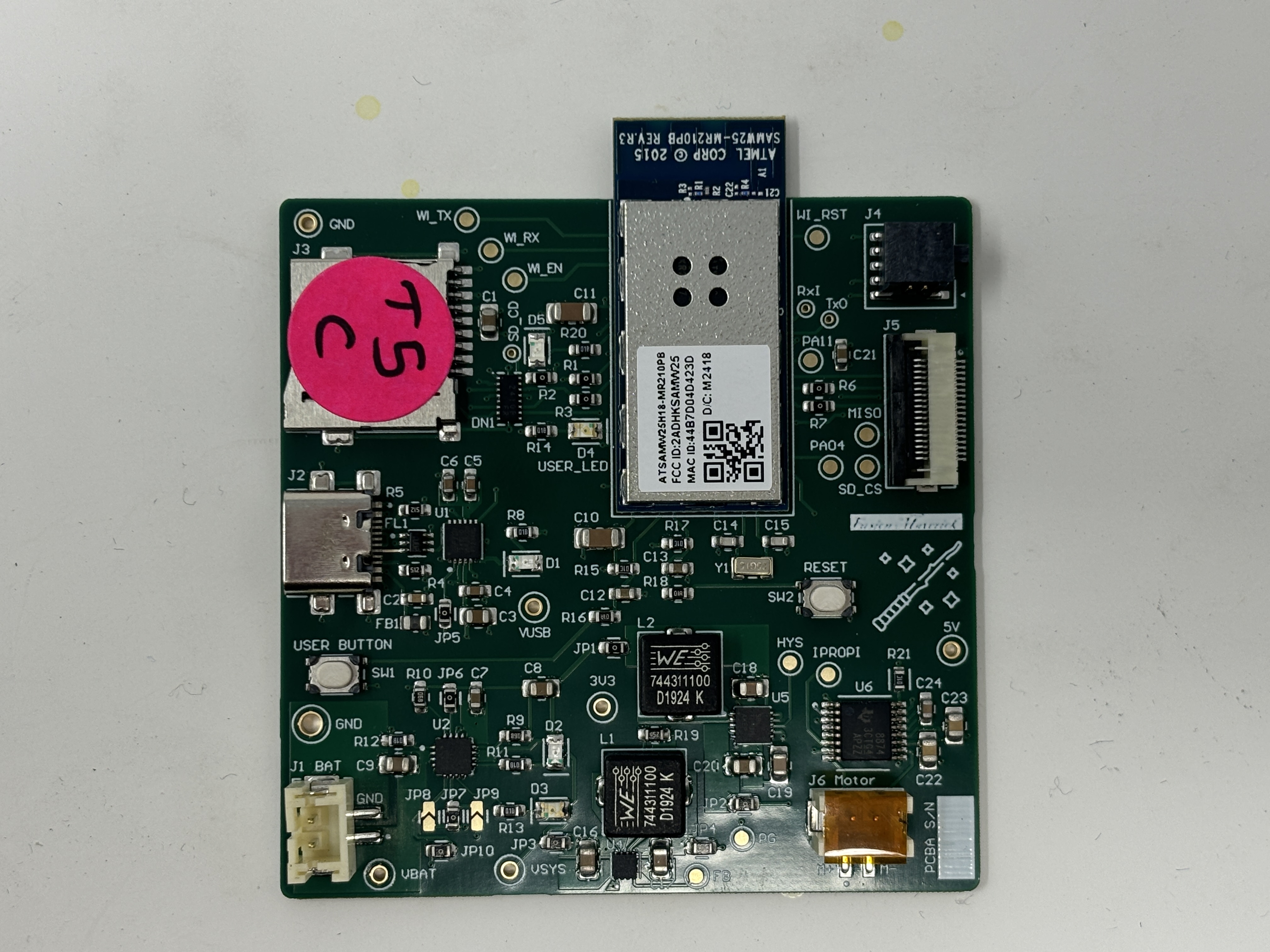
-
- The standalone PCBA, bottomp:
-
magic wand:
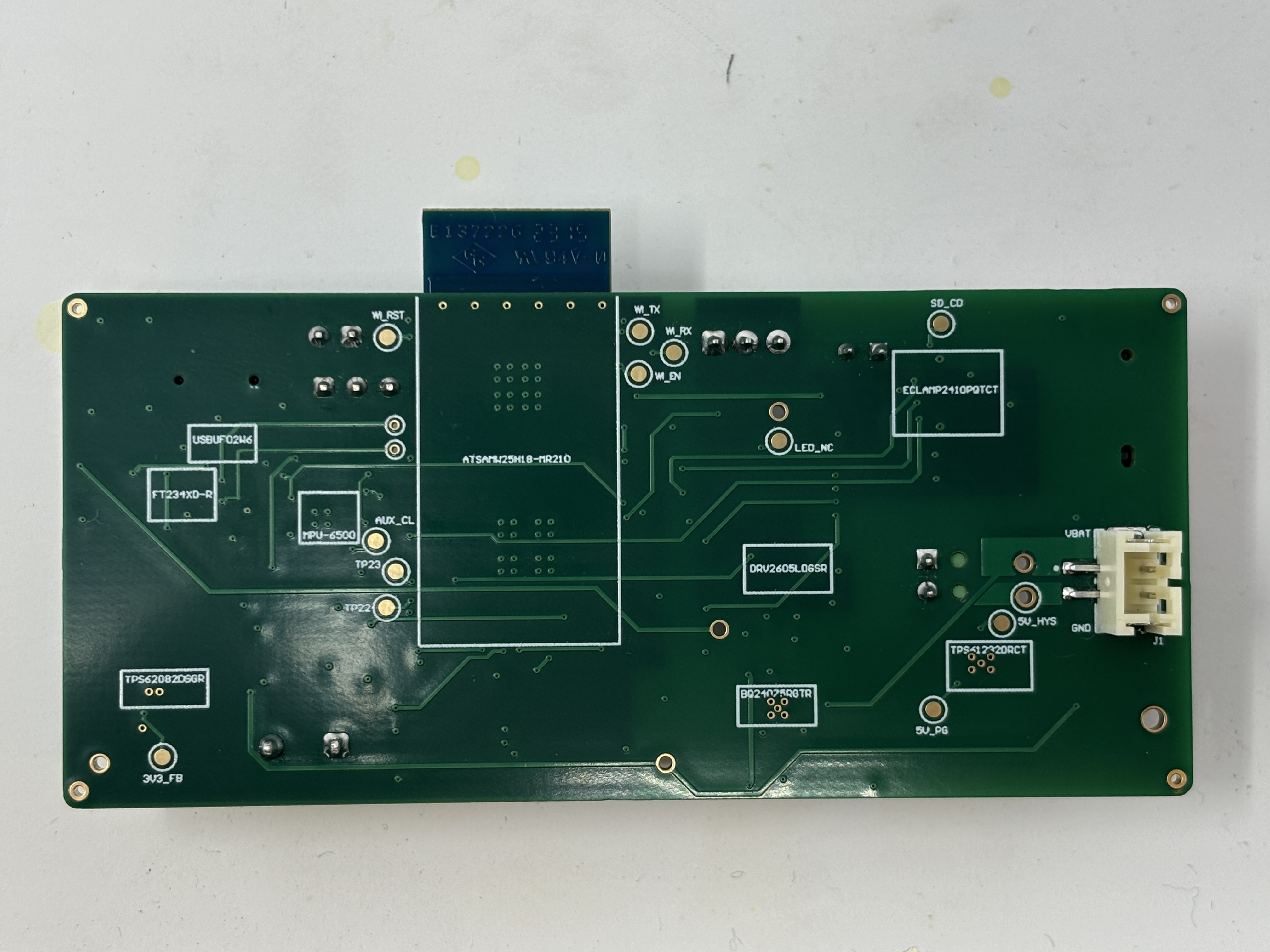
-
actuator:
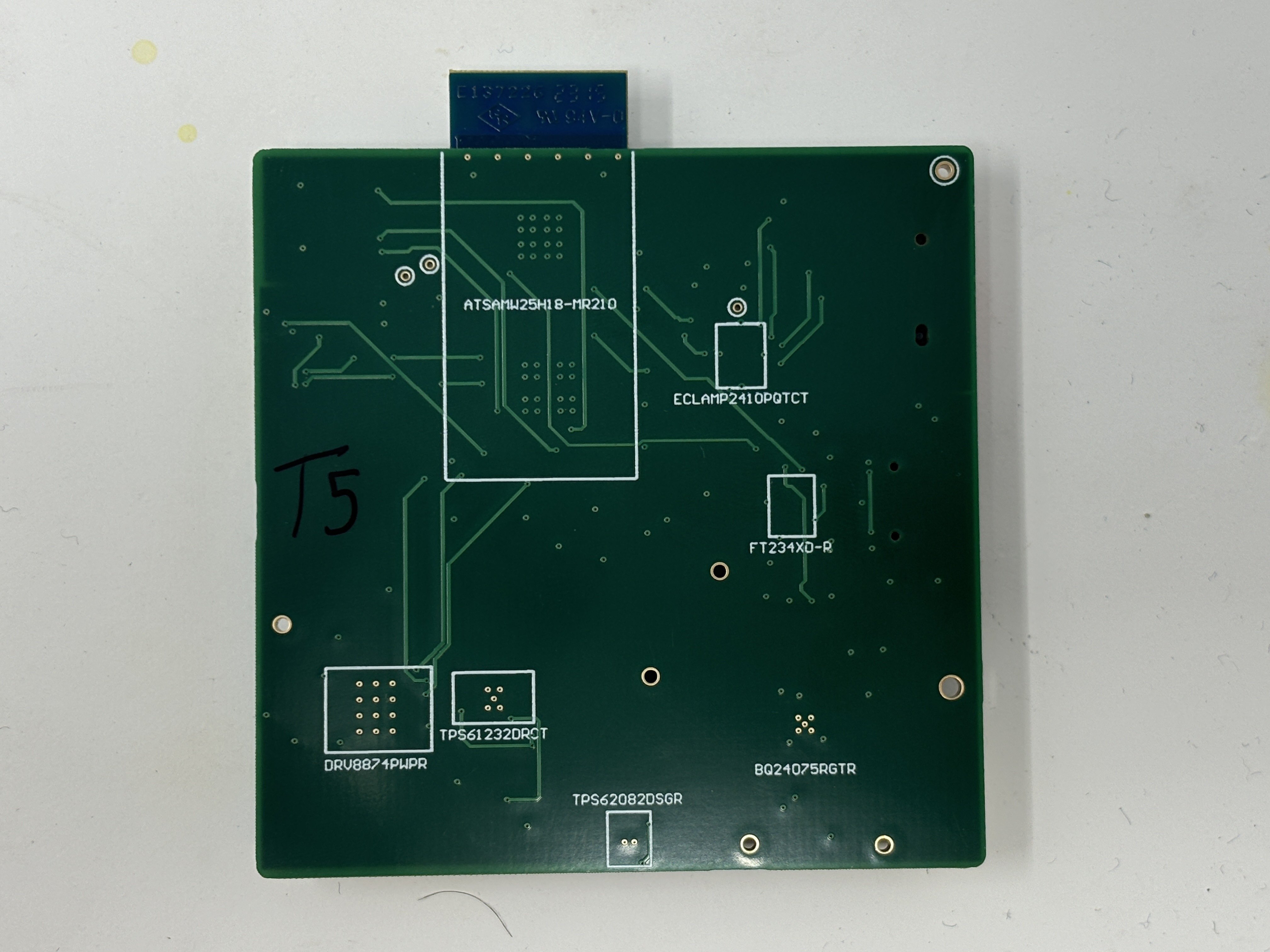
-
- Thermal camera images of boards under load:
-
magic wand:

-
actuator:

-
- Altium Designer board layout 2D view:
-
magic wand:
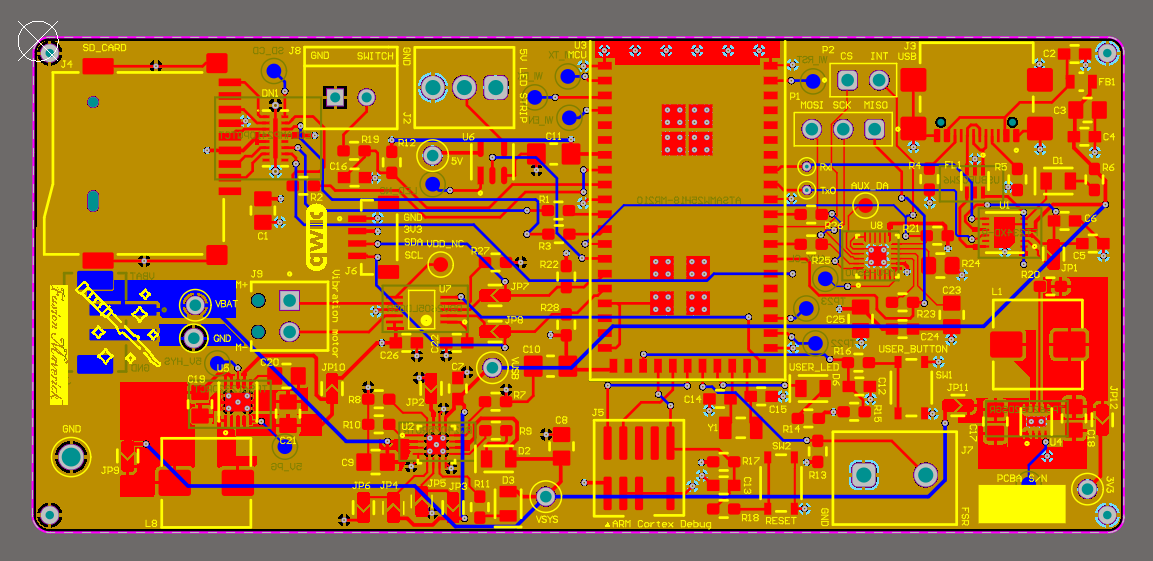
-
actuator:
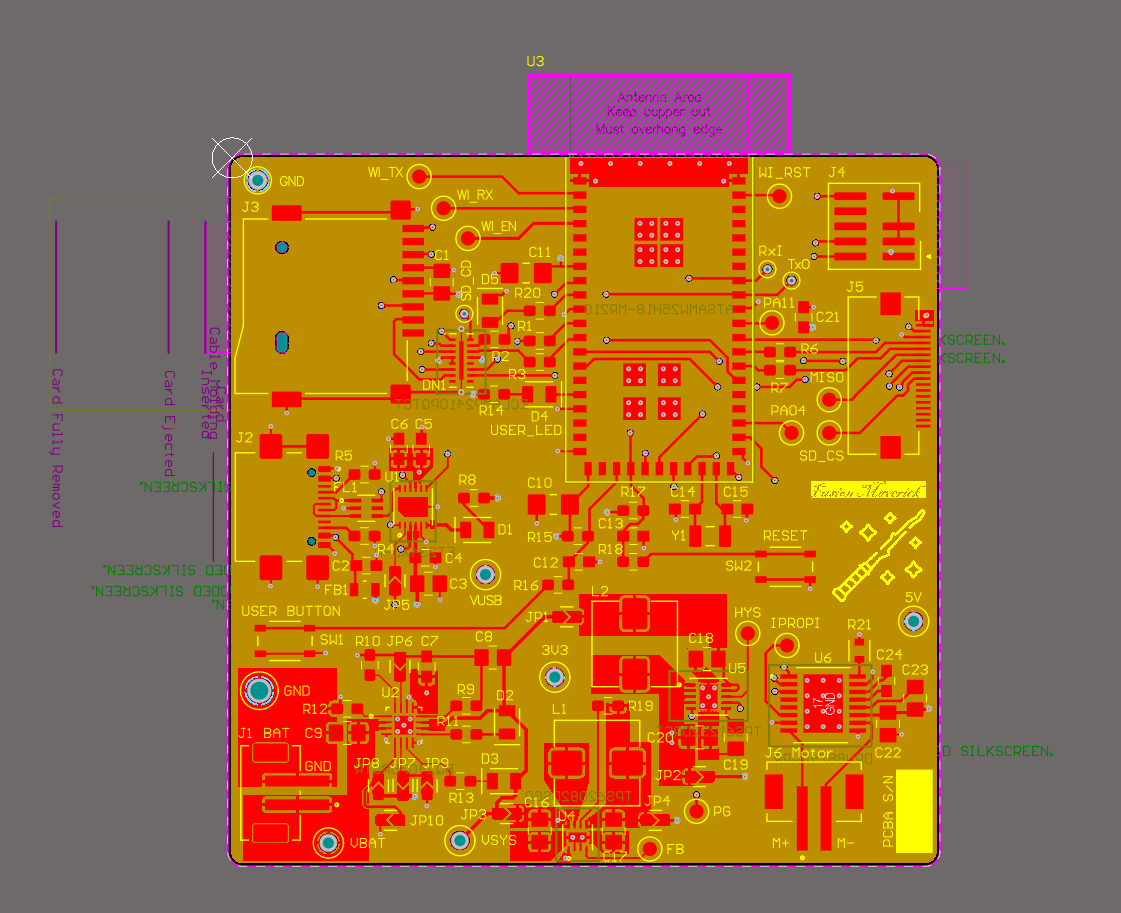
-
- Altium Designer board layout 3D view:
-
magic wand:
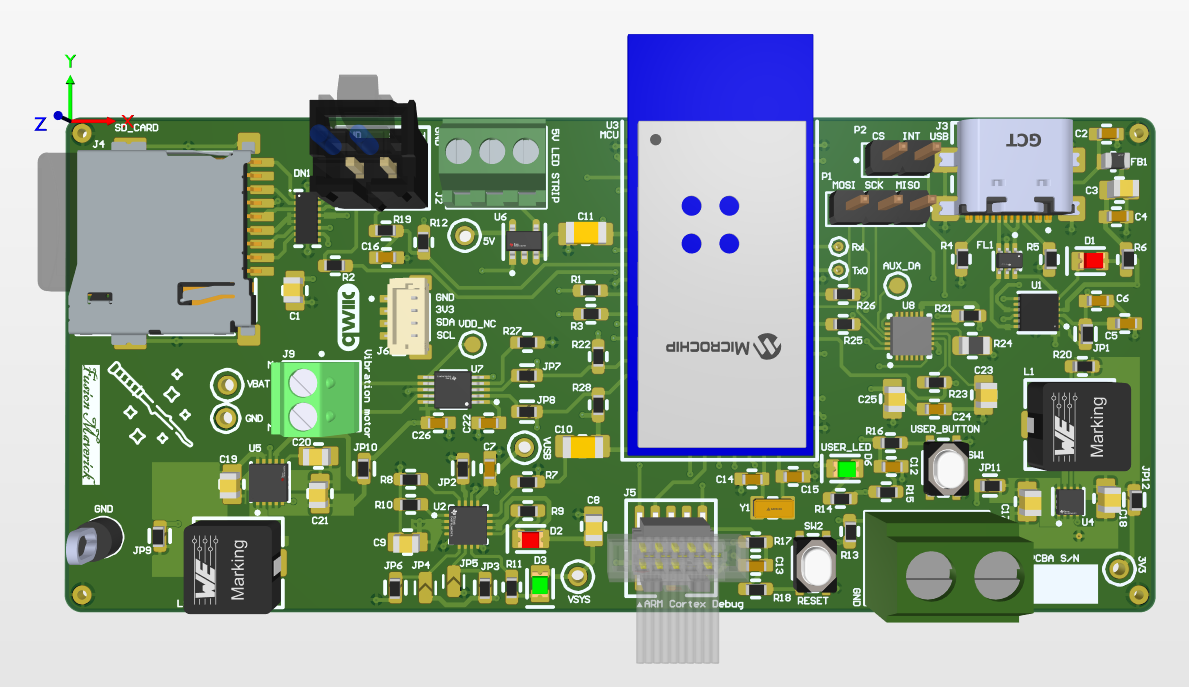
-
actuator:
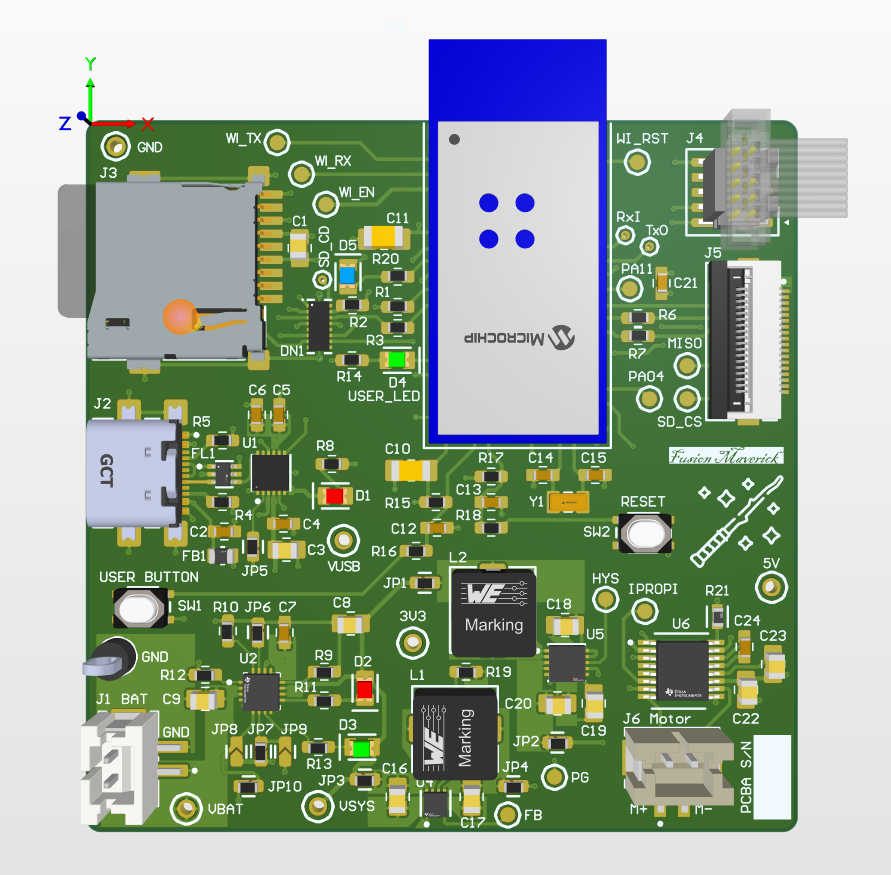
-
- Node-RED dashboard:
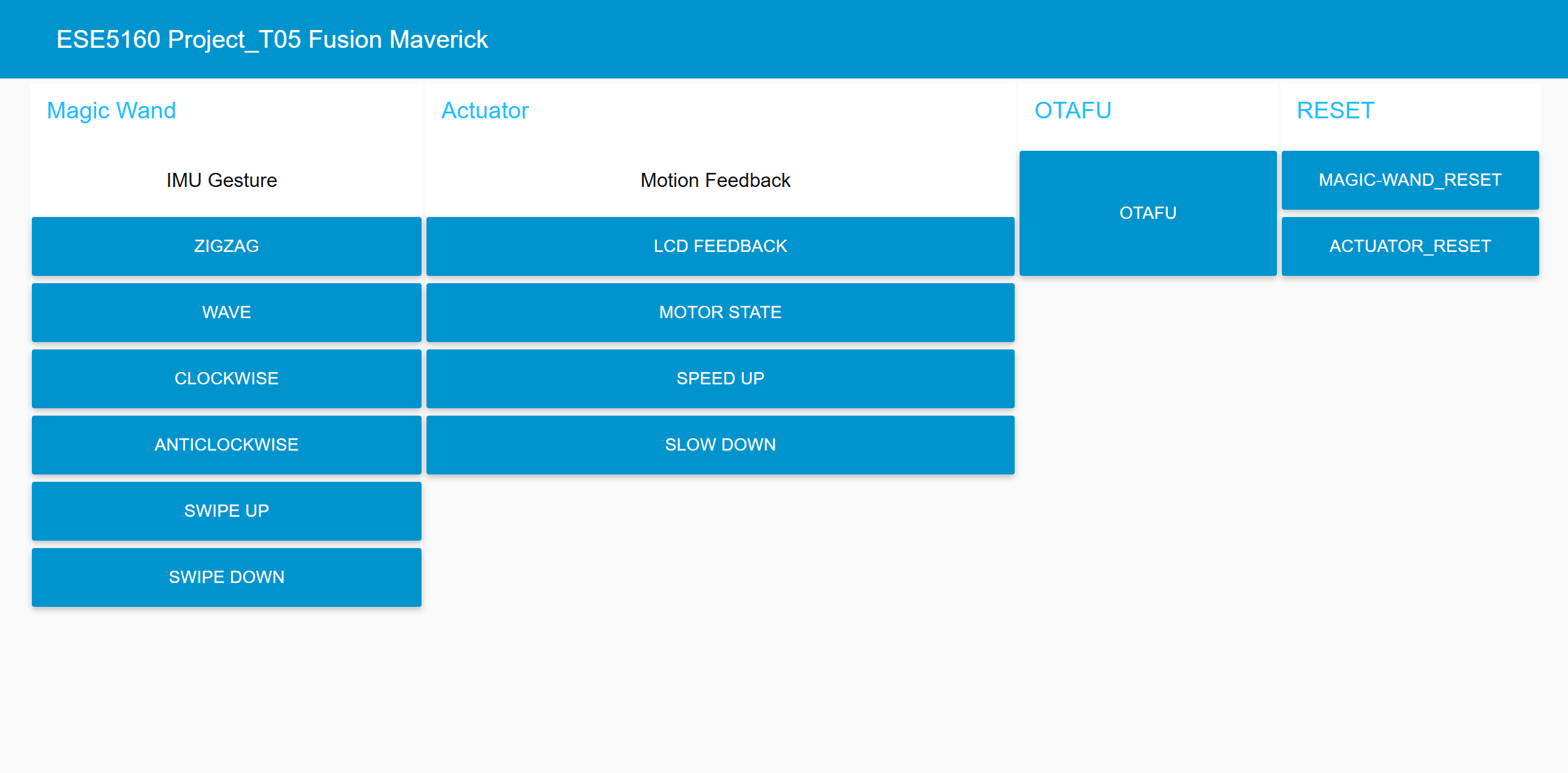
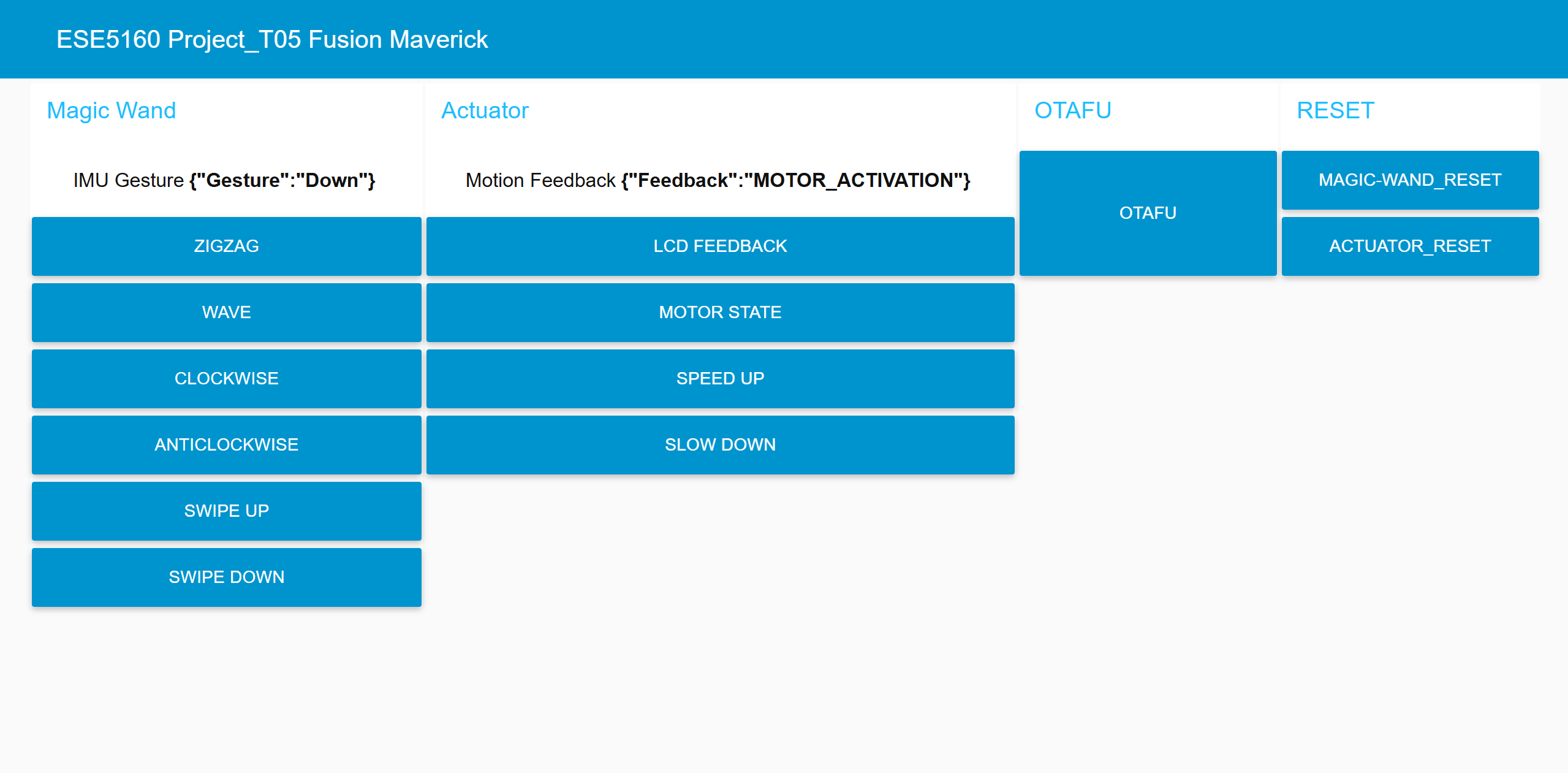
- Node-RED backend:
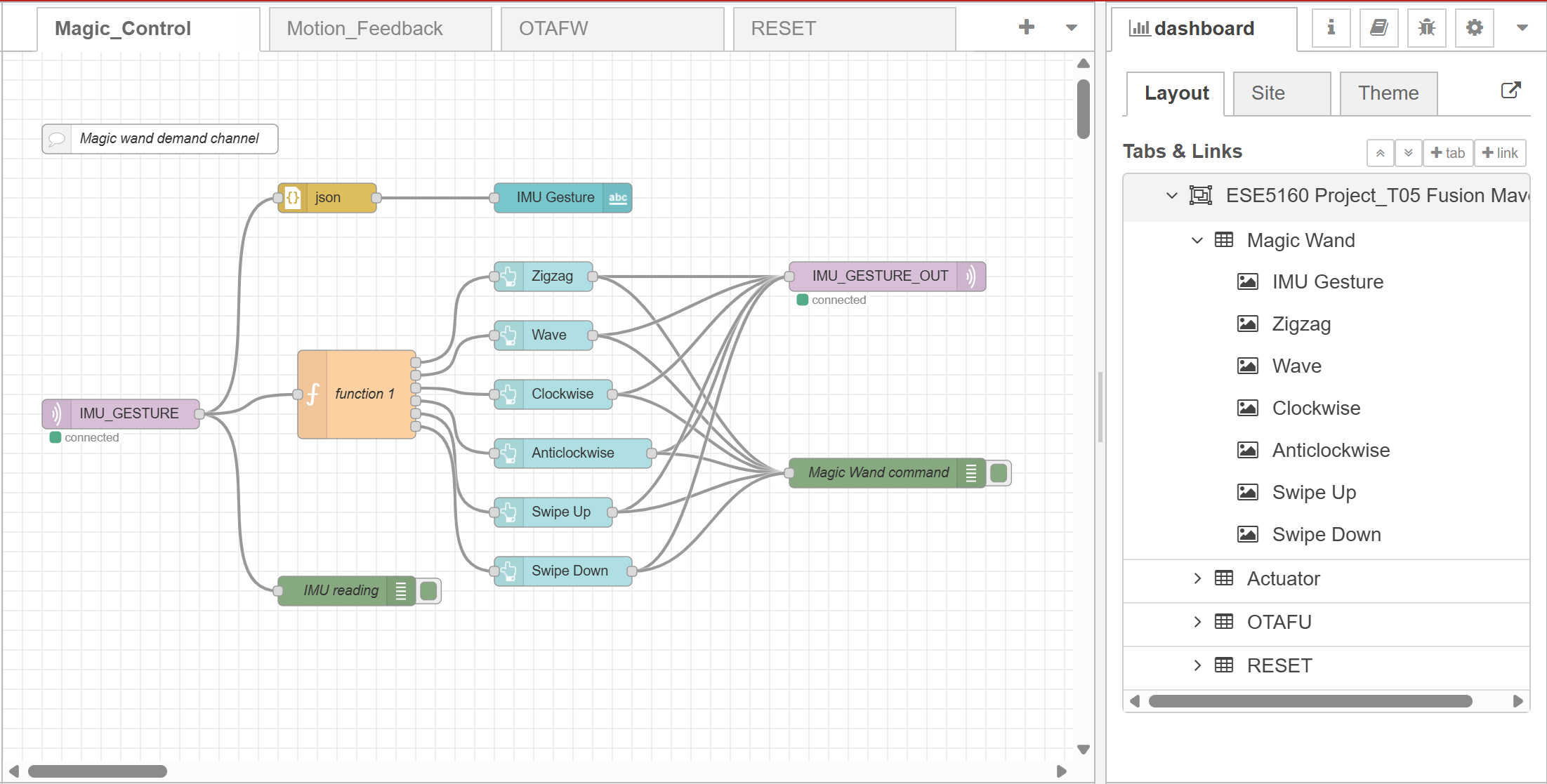
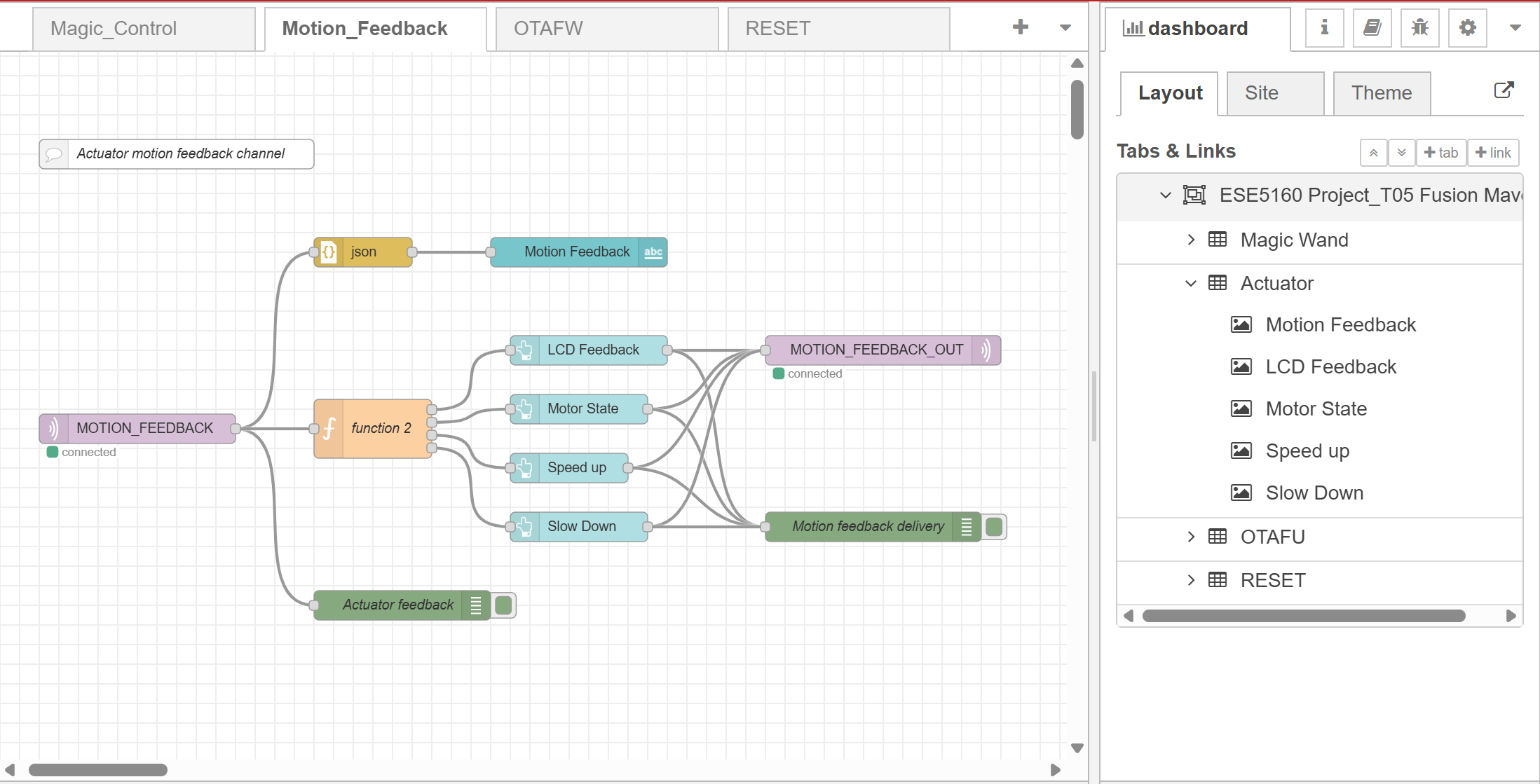
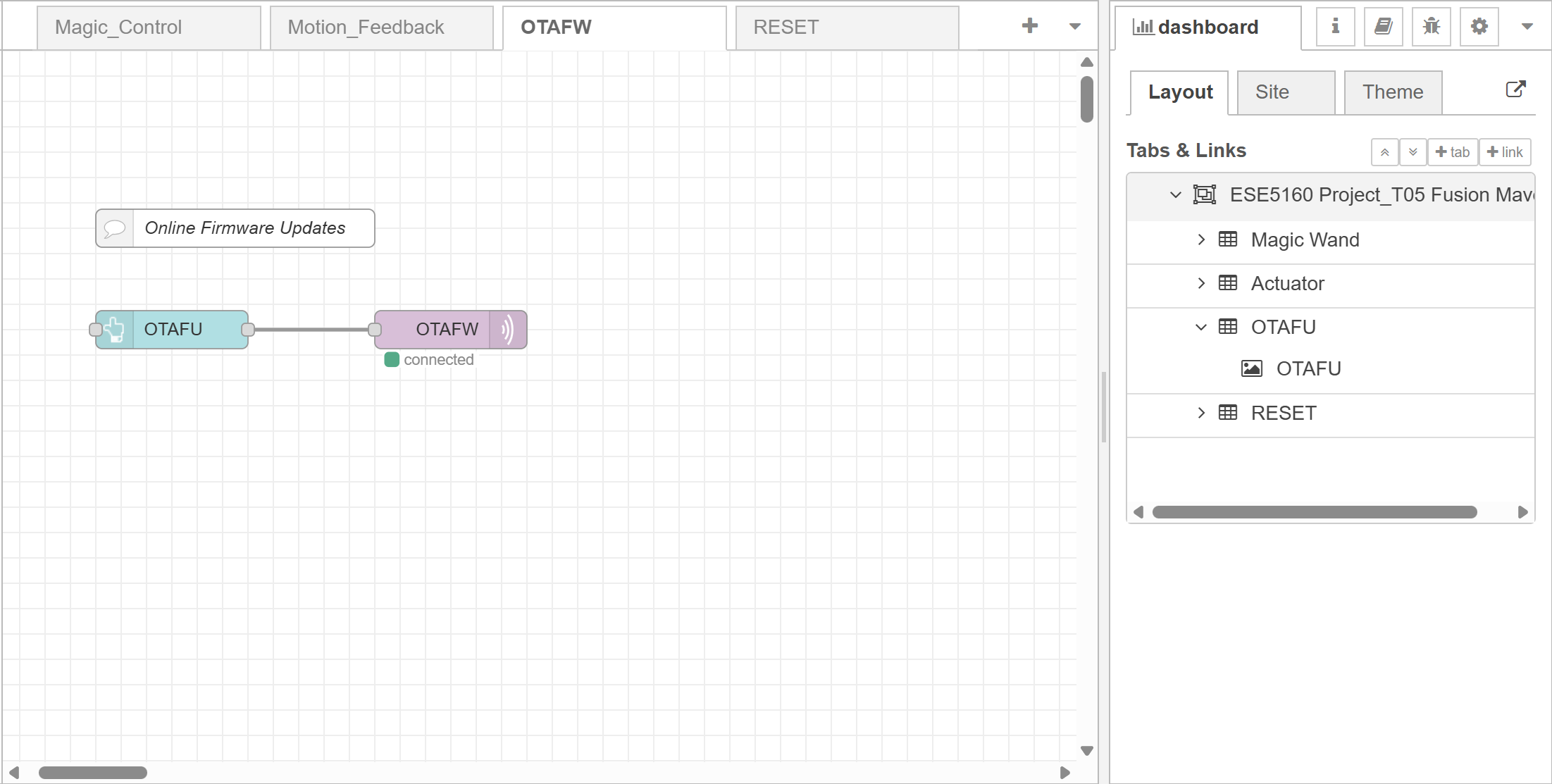
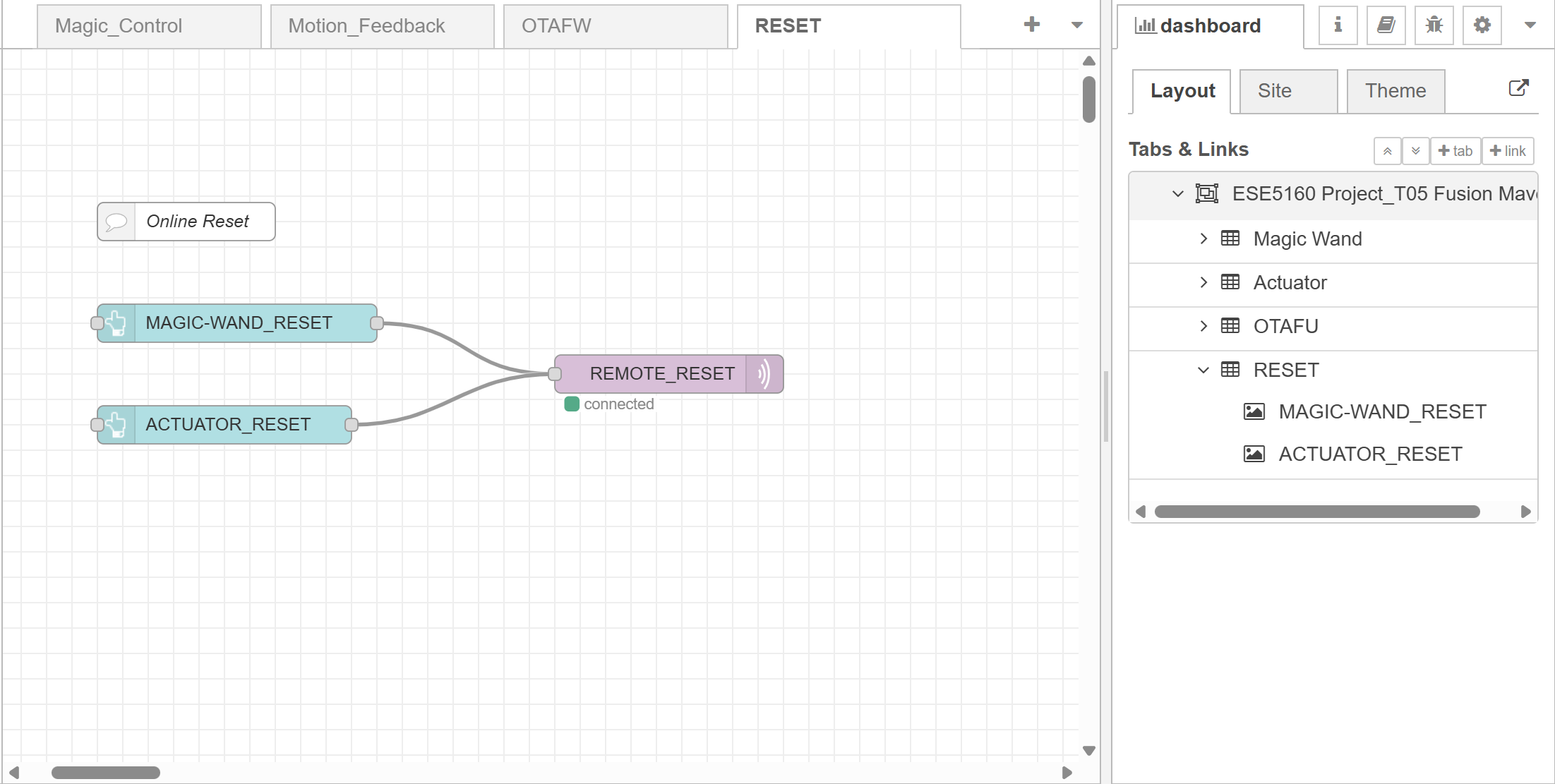
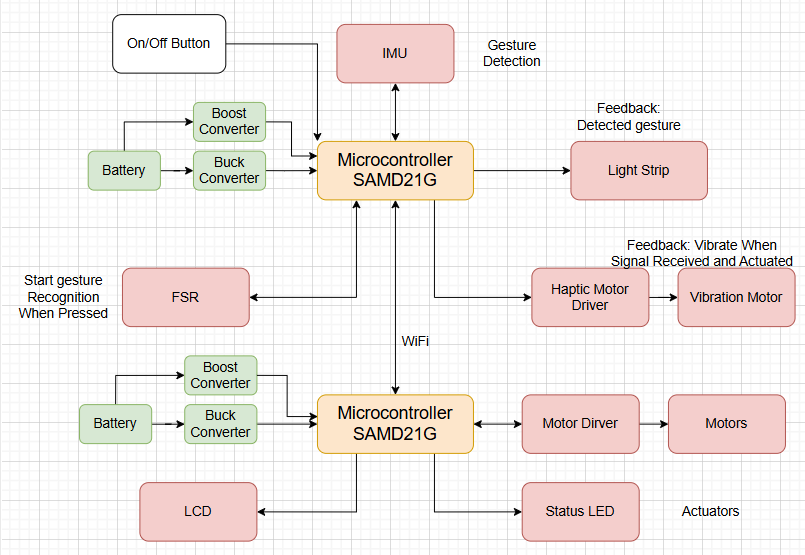
- Block diagram:

Codebase
- link to final embedded C firmware codebases:
- link to Node-RED dashboard code.